In addition to setting a hostname, it is good practice to set a fixed IP address to network hosts that provide services to other hosts. This way, a client will be able to use the same IP address for all its requests to the server, instead of first doing a lookup request to the DHCP server.
To set a fixed IP address for your Raspberry Pi, you will need to login to your router’s admin panel. Every router has an admin panel with its own “branded” design elements, but in general there is a page titled “DHCP” or “Bind IP” that allows you to edit the configuration of a host’s IP address.
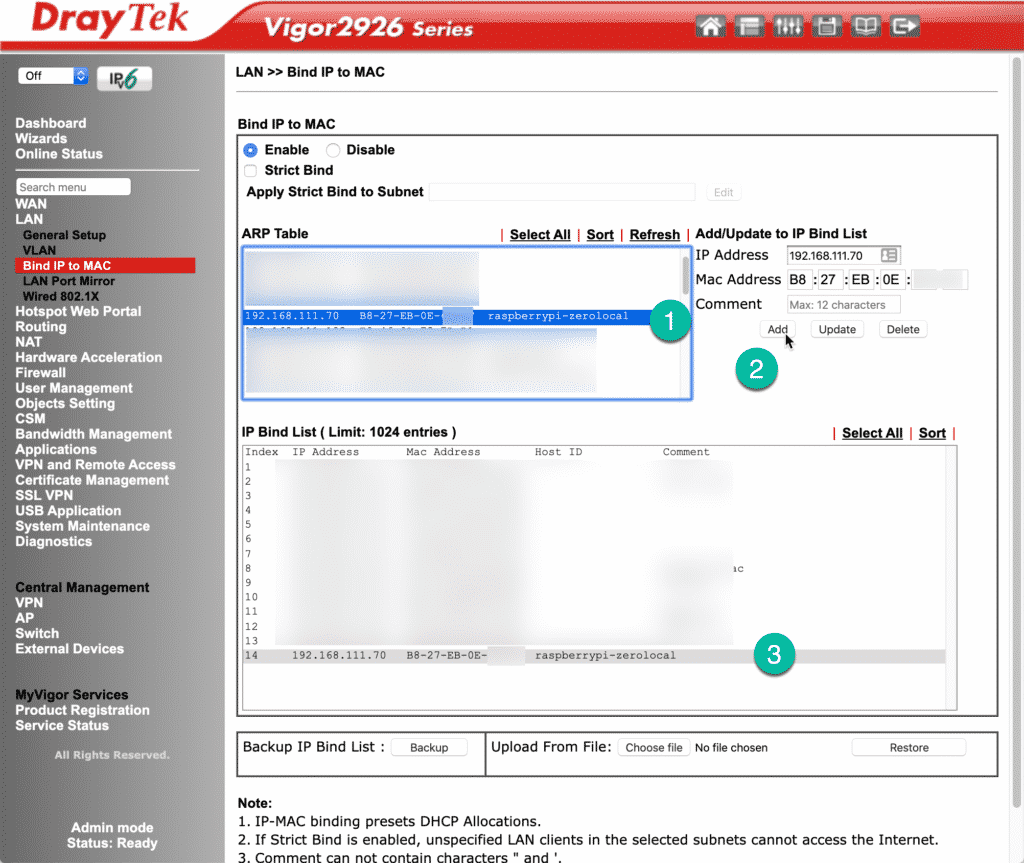
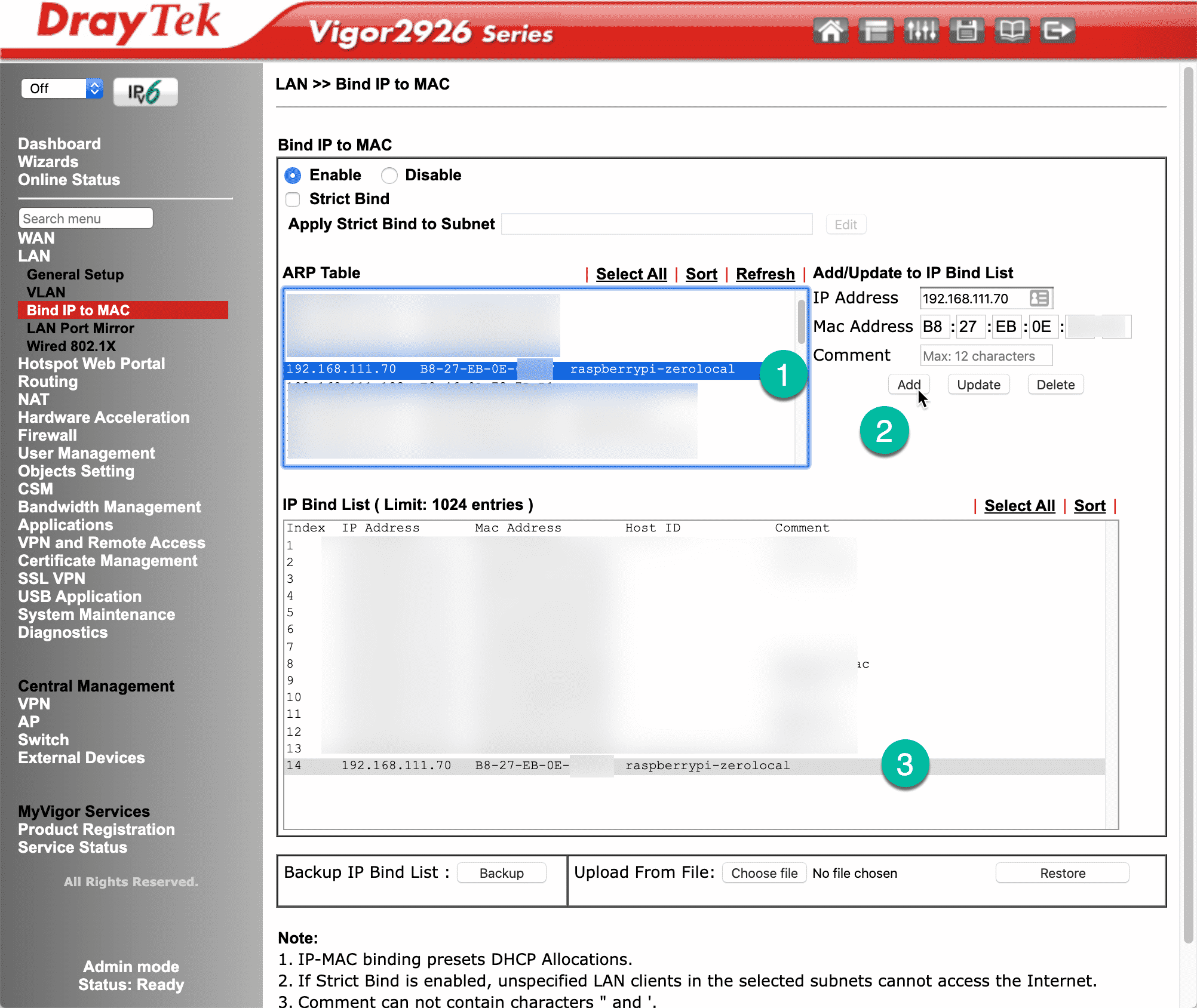
In the screenshot below you can see the relevant page in my router’s administration panel. This page is available under the LAN menu item.
To bind an IP address to a MAC address, first select the Raspberry Pi by identifying its hostname from the ARP Table (“1”), then click on the “Add” button (“2”), you may change the IP address to something else, or accept the one that DHCP has already assigned).
In the IP Bind List box, you can now see the fixed IP address for your Raspberry Pi ("3").